Jump To Section
- 1 Customer Pain vs. Legacy Platforms: Bridging the Expectation Gap
- 2 Why Billing Is the Perfect Starting Point for Gen AI in Telecom
- 3 Case in Point: How Leading Telecoms Are Solving Support and Billing Challenges
- 4 The 4-Step AI Integration Playbook
- 5 Final Takeaway: Next Step in Modernizing Telecom Billing
- 6 FAQs
Despite spending millions on digital and aggressive investments into self-serve apps and AI pilots, billing remains the number one source of customer confusion and support volume for telecom providers.
It accounts for up to 50% of contact centre calls, and yet most billing systems haven’t meaningfully evolved in over a decade.
The challenge isn’t a lack of ambition. It’s execution on a stack that was never meant to deliver modern experiences.
Legacy billing systems weren’t built for today’s customer expectations, or for AI. But that doesn’t mean you have to rip and replace your core infrastructure. You just need a smarter way to bridge the gap.
This playbook outlines a low-risk, high-impact approach to using Generative AI to modernize telecom billing support without disrupting the core systems that keep you running.
Drawing on real-world implementations, integration frameworks, and lessons from industry leaders like TELUS and Verizon, the steps provided in this guide are designed to aid transformation executives who need results: reduce support volume, improve digital containment, and turn billing from a liability into a loyalty driver.
Customer Pain vs. Legacy Platforms: Bridging the Expectation Gap
Customers expect clarity. But most billing systems were designed when transparency meant mailing a paper invoice. These legacy billing systems are outdated and inflexible, struggling to support the demands of modern, digital services and complex pricing models.
Today, customers want to tap their screen and get a simple, human explanation of their charges.
Accurate billing is essential for preventing revenue leakage and maintaining customer trust, but legacy billing systems often fall short in delivering precise, real-time invoicing. Instead, customers wait on hold, navigate IVRs, and eventually talk to agents reading off of scripts. That’s not customer experience. It’s attrition in progress.
The Billing Pain Point: Where Legacy Hurts the Most
For decades, companies have relied on legacy software — including IVRs, outdated CRMs, and antiquated ticketing systems — to manage customer interactions.
Telecommunications providers, in particular, struggle with outdated systems that hinder their ability to innovate and deliver modern experiences.
While these tools once revolutionized service efficiency, they now serve as a primary roadblock to meeting modern customer expectations.
Legacy IT systems are a double-edged sword in telecom: deeply ingrained in operations but often the biggest roadblock to exceptional customer service. Fragmented, siloed legacy databases and CRM/billing platforms impede seamless support and negatively impact customer care.
Agents grapple with slow interfaces and incomplete customer data, leading to repetitive information requests and frustration for both staff and customers. Many agents are also bogged down by routine tasks due to legacy systems, further reducing their efficiency.
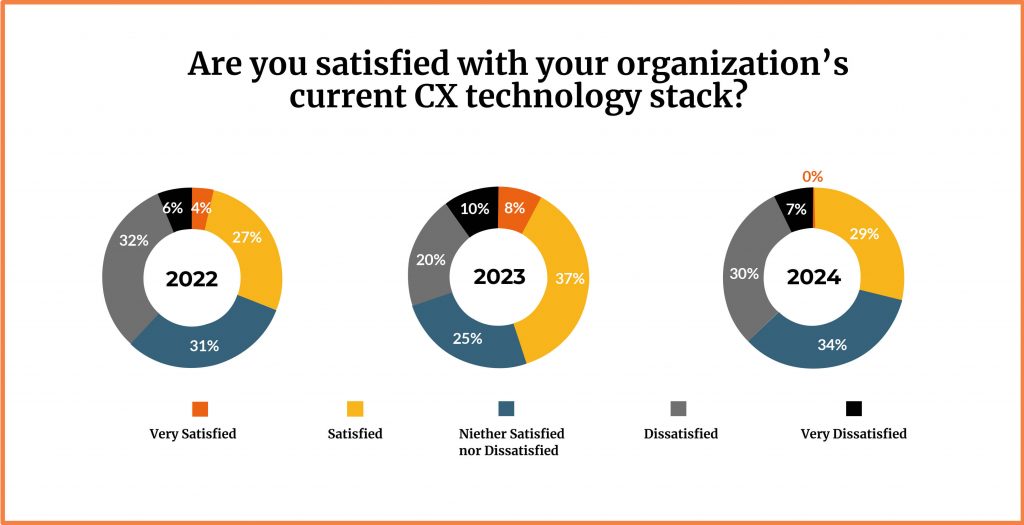
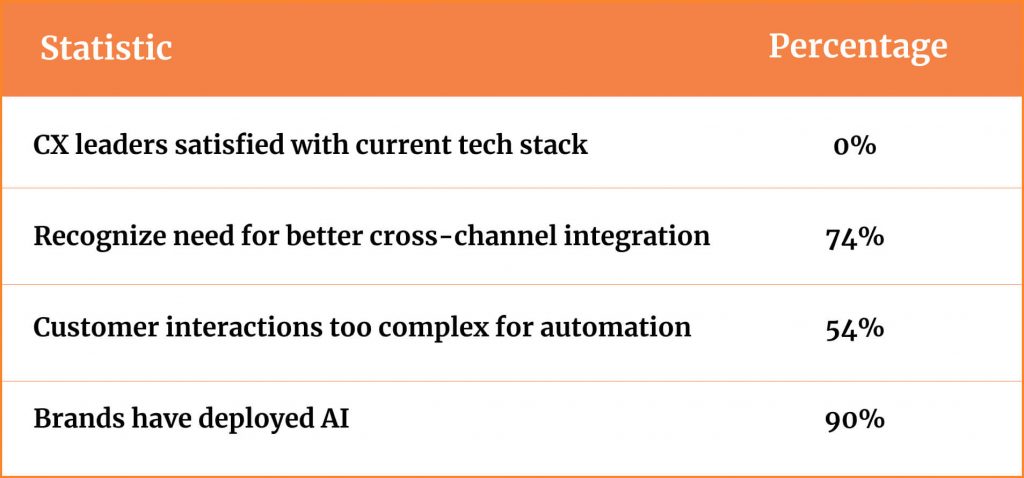
According to a 2024 ExecsInTheKnow study, 90 percent of telecoms have deployed AI, yet 74 percent still cite poor cross-channel integration as a CX blocker.
Billing isn’t back-office anymore. It’s front-line CX. And it’s where Generative AI can deliver fast, measurable ROI.
Why Billing Is the Perfect Starting Point for Gen AI in Telecom
Telecom companies often underestimate how much damage unclear billing can do, until the call volumes spike, agent turnover increases, and customers quietly leave.
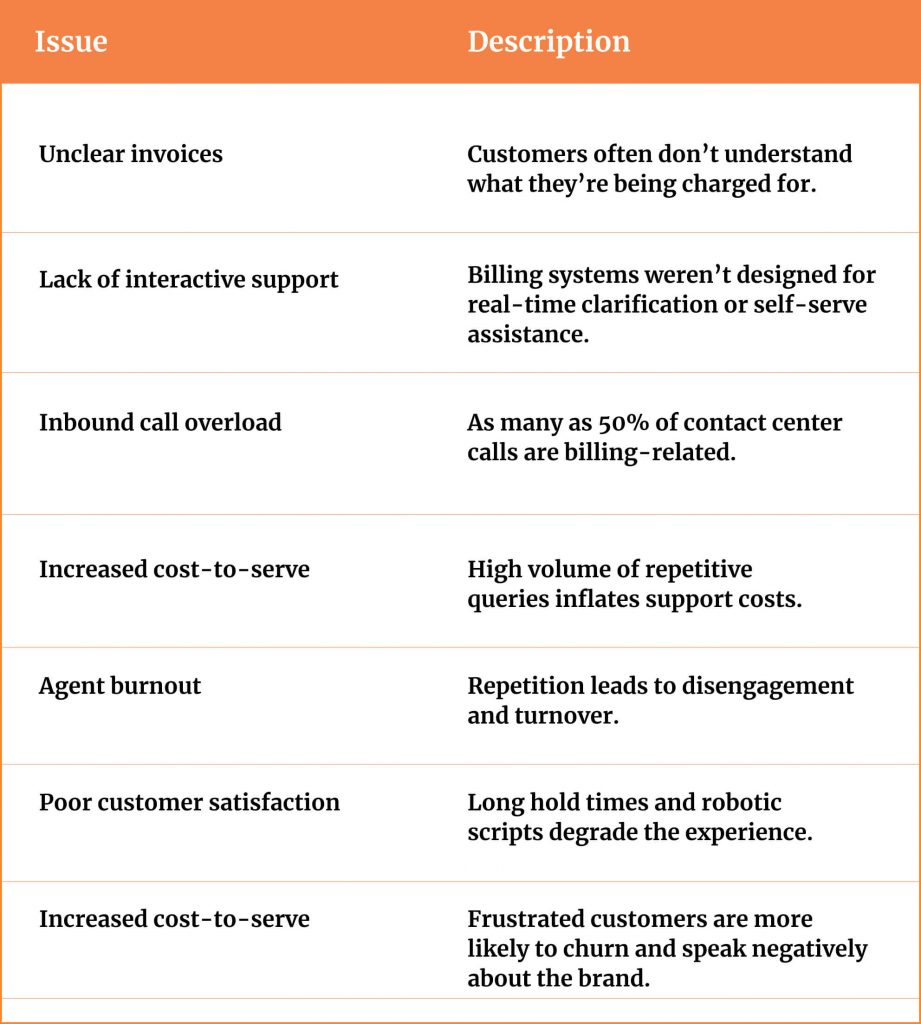
The key challenges telecoms face include:
Unclear invoices
Most telecom bills are designed for internal accuracy, not customer clarity. Charges are often presented in technical or fragmented terms, leaving customers confused and frustrated about what they’re actually paying for. This erodes trust and creates unnecessary service volume.
Lack of interactive support
Legacy billing platforms were never built to support real-time Q&A, contextual explanations, or self-serve functionality. When customers have questions, they face slow-loading portals or are funneled into call queues with no intelligent assistance.
Inbound call overload
As much as 50% of telecom contact centre volume stems from billing-related issues. These repetitive queries clog support channels, delay service for other issues, and generate massive downstream costs.
Increased cost-to-serve
Repetitive billing inquiries tie up live agents, drive longer average handling times, and inflate staffing requirements—without adding any value to the customer experience.
Agent burnout
Support teams often spend their day walking customers through line items, over and over. This kind of repetitive work leads to disengagement, higher turnover, and increased training costs.
Poor customer satisfaction
Long wait times, impersonal responses, and limited digital support options create a frustrating experience. Customers feel ignored and undervalued, especially when billing is the only regular interaction they have with their provider.
Brand erosion
When billing becomes a pain point, it doesn’t just impact NPS. It damages brand perception. Frustrated customers are more likely to churn and speak negatively about their provider in online reviews or social channels. To reduce churn rate, here are 5 steps to apply to your customer journeys that will garner trust and brand loyalty.
Here’s the opportunity: Generative AI can explain billing in natural language, personalized to each user, grounded in actual account data, and available 24/7. AI powered virtual assistants are now being used to handle billing inquiries, improve support responsiveness, and reduce operational costs, fundamentally enhancing the way telecoms interact with customers.
It doesn’t replace your agent. It scales them.
It doesn’t require a full IT overhaul. It sits on top of your existing stack, connecting to your CRM and billing systems via APIs.
I’ve helped design AI pilots for telecoms in this exact space. The results? Fewer calls. Higher app usage. Customers who feel heard. Agents who can focus on solving real problems, not explaining line items.
Case in Point: How Leading Telecoms Are Solving Support and Billing Challenges
Leading telecom companies are beginning to deploy generative AI solutions to address the above challenges.
Case studies from North American carriers illustrate how AI can elevate customer-facing services:
TELUS (Canada): Self-service Boost through Chatbot Integration
TELUS introduced a GenAI-powered customer support chatbot in 2024 using Azure OpenAI and the Fuel iX engine. The tool answered over 50,000 queries within weeks, enabling 28% more customers to self-serve successfully. Built on responsible AI principles and Privacy by Design, it integrates 1,000+ vetted support articles and underwent rigorous testing.
Verizon (USA): Live Agent Augmentation with GenAI
Verizon adopted GenAI to augment—not replace—its 28,000 customer service agents. The AI assistant, powered by Google’s LLMs, listens to live calls and recommends real-time responses or next-best actions. Since scaling the solution enterprise-wide in early 2025, the company has reported a 40% increase in service channel sales. The initiative demonstrates how generative AI can quietly and effectively work behind the scenes to support human agents, streamline workflows, and increase upsell potential without requiring customers to interact directly with a bot.
Amdocs (Industry Vendor): GenAI Platform Streamlines Billing Queries
Amdocs developed the ‘amAIz’ GenAI platform to tackle telecom billing queries using LLMs fine-tuned on billing data. By applying Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) and deploying on NVIDIA infrastructure, they improved billing answer accuracy and cut inference costs by 40%.
Vodafone (Global): AI Chatbot Reduces Wait Times
Vodafone used AI-powered chatbots to manage common billing and plan inquiries, reducing customer wait times by over 50%. This highlights how GenAI can rapidly improve self-service efficiency.
For a detailed guide into making self-serve more interactive and effective, read this article on Breaking the Telecom Self Service Barrier with AI-Powered Hubs.
AT&T (USA): Backend AI for Network Reliability
AT&T focused on backend AI for network optimization and predictive maintenance. Though not customer-facing, the improvements enhanced service reliability, indirectly benefiting customer experience.
Whether customer-facing or agent-augmenting, AI in telecom consistently improves customer experience, shortens resolution times, and reduces operational cost, without needing to replace legacy systems.
The 4-Step AI Integration Playbook
Implementing GenAI in a telecom environment isn’t about chasing the next big trend. It’s about applying proven, scalable techniques to modernize real, persistent challenges.
The following four steps represent a pragmatic, low-risk framework for layering AI onto your existing systems, helping you move from pilot to production without disrupting operations or customer trust.
Step 1: AI Integration Strategies for Legacy Telecom Systems
Implementing a generative AI solution in a legacy telecom environment requires careful integration planning. Legacy CRM, billing, and support systems often lack modern APIs and can be “walled gardens” of data.
Several requirements and best practices have emerged:
Data Integration via APIs or Middleware
Bridging AI into legacy apps typically involves creating custom APIs or middleware layers that can communicate with older systemsn-ix.com.
Many legacy BSS/OSS platforms weren’t built to talk to external AI services, so companies like N-iX adopt a phased integration: identify critical data (e.g. customer profile, bill details), then develop API endpoints or connectors to expose that data to the AI platformn-ix.comn-ix.com.
For example, a chatbot needs an API to pull a customer’s latest bill from the billing system, or to query usage data from a CRM, in order to answer “Why is my data overage fee $20?”
Connection to Knowledge Bases
Many customer queries (especially for support) can be handled by referencing existing documentation – FAQs, support articles, device manuals, etc.
A successful GenAI deployment will integrate with the telecom support knowledge base or document repositories.
By plugging into knowledge sources, the AI can provide up-to-date, accurate answers that align with company policy, effectively expanding the legacy help libraries with an intelligent interface.
Legacy CRM and Billing Hooks
Integration isn’t only about data retrieval; it may also involve allowing the AI to perform actions on legacy systems via APIs.
For example, if an AI assistant is handling a billing dispute, it might need to trigger a credit or open a support ticket. Thus, exposing certain write operations through secure APIs or RPA (robotic process automation) bots could be necessary.
Compatibility and Performance
Legacy systems might not handle high-frequency API calls well. The integration design should account for caching of common data (to reduce load on an old database) and perhaps use asynchronous queues for any heavy processing. Also, latency is a concern – customers expect quick answers, so the integrated AI system must fetch legacy data and return a response within a few seconds. This might entail optimizing queries or upgrading parts of the legacy stack (e.g., indexing the billing records for fast search).
Phased Rollout and Testing
Given the fragility of some legacy environments, it’s wise to pilot AI integrations in a limited scope first. For instance, connect the AI to a subset of data (or a copy) and test with employees, or roll out the chatbot to a small region’s customers before full scale
Integration is often the hardest part of bringing GenAI into a legacy telco app. But with well-defined APIs, data mapping, and a cautious rollout, even decades-old BSS/OSS components can work in tandem with cutting-edge AI.
In fact, successful projects report that legacy modernization can happen in parallel – implementing “custom APIs to bridge legacy systems with AI platforms and gradually modernizing the IT infrastructure” go hand-in-hand.
Step 2: Feedback Loops and Continuous Learning
Deploying an AI solution is not a “set and forget” endeavor.
Especially in telecom, where products, policies, and customer behaviors change continually. To truly succeed, a generative AI system needs a feedback loop for continuous learning and optimization. Key design considerations include:
Ongoing Training Data Updates
The AI model should be regularly updated with new data. Telecom offerings (e.g. new plans, pricing changes) and support issues evolve, so the knowledge base and training corpus must stay current.
GenAI agents are continuously updated with new types of billing queries and refined responses based on customer interactionssubex.com. This might involve fine-tuning the LLM on transcripts of unresolved queries or retraining classification models as new support topics emerge.
User Feedback Integration
Collect explicit feedback from users about the AI’s answers. This can be as simple as thumbs-up/down ratings after a chatbot interaction, or a survey asking if the explanation was helpful. Negative feedback (or cases where the customer still calls support after using the AI) should be analyzed to identify failure modes.
Human Oversight and Agent Review
A feedback loop often includes human-in-the-loop review. Difficult queries that the AI couldn’t handle (e.g. it got handed off to a human agent, or it gave an unsure response) should be flagged.
Then a subject matter expert or trainer can provide the correct resolution, which is fed back into the AI’s knowledge. This could mean adding a new Q&A pair to the database or updating the model’s response patterns. Such supervised feedback closes the loop so that, over time, the AI’s performance on edge cases improves.
Multi-Turn Context Handling
Telecom customer inquiries often involve multi-turn conversations (follow-up questions, clarifications). The AI design should maintain context across turns and learn from the flow of dialogs.
If users frequently ask a particular follow-up question after a certain answer, that’s a signal the initial answer wasn’t clear enough. The system can be tweaked to preempt that follow-up. Robust context management (using conversation history in prompts or memory) and analyzing conversation logs help the AI get “smarter” in carrying a natural dialogue.
Performance Monitoring and Iteration
Define metrics for the AI’s performance (resolution rate, customer satisfaction scores, average interaction time, escalation rate to human, etc.) and monitor them continuously. A drop in any metric might indicate the AI isn’t keeping up with new issues or something in the environment changed (e.g., a new device release causing questions the AI can’t answer yet).
A well-designed feedback loop might look like this: The AI answers a billing question. The customer indicates it was not helpful. That query along with the context is logged. Later, a trainer reviews it, sees the AI missed that the customer had a one-time charge for equipment. The trainer adds a rule or example to teach the AI to check for equipment charges in such cases.
Next time a similar question comes, the AI identifies and explains the one-time charge correctly, and the customer is satisfied. Over thousands of interactions, this process (sometimes automated, sometimes with human help) leads to an AI assistant that continuously learns from its mistakes and adapts to new scenarios.
Step 3: Technology Stack for AI
Implementing AI in a legacy environment requires assembling a technology stack that can interface with old systems while delivering modern AI capabilities.
The following components are key:
Large Language Models (LLMs) for Natural Language Interaction
At the heart of generative AI in customer service is a language model that can understand free-form text or speech and generate human-like responses. Telecom use cases benefit from LLMs because of the need to interpret diverse customer queries like, “My internet is down” or “Explain this charge on page 3 of my bill”, and respond conversationally.
Options include using an API to a hosted LLM (e.g. OpenAI GPT-4, Azure OpenAI Service or fine-tuning an in-house model. Some carriers might choose open-source LLMs fine-tuned on telecom data for data privacy reasons. It is vital to master conversational AI to ensure such customer interactions are effective. Here are 6 steps to have smarter customer interactions through cnversational AI.
Machine Learning for Personalization and Analytics
Beyond the chatbot/LLM itself, a robust AI solution will include ML models that analyze customer data and drive personalization. Telecoms sit on massive data (usage records, network performance, customer profiles) that can be mined for insights.
The tech stack should have components for:
- Predictive Analytics: Models to predict churn risk, customer lifetime value, or propensity to upgrade.
- Personalization Engine: Tools to decide the best offer or response for a given customer. This can be rule-based initially, but more advanced setups use reinforcement learning or multi-armed bandits to personalize in real-time.
- Analytics Dashboard: It’s often useful to include a dashboard for business users to monitor how the AI is performing and to tweak personalization rules. This could be a custom web dashboard or integration with existing analytics tools.
Responsible AI and Security Components
Given the sensitive nature of telecom data and the direct customer impact, the stack must include features to enforce responsible AI practices:
- Content Filtering and Guardrails: The system should filter out or avoid any inappropriate or harmful content in AI responses.
- Privacy and Data Protection: The stack should implement encryption for any data in transit between the AI and legacy systems. If using a third-party LLM API, sensitive customer data should be redacted or tokenized before sending, unless the API is housed in a secure environment.
- Opt-Out and Transparency Mechanisms: Responsible AI also means giving users control. The app’s UI/UX (part of the tech stack from an end-user perspective) should disclose that an AI is assisting them and offer a path to a human agent if desired.
Platform and Infrastructure
Underlying all these components is where they run. Many telcos choose a cloud-based deployment for agility – e.g., using AWS or Azure to host the AI services next to their legacy data (which might also be migrated or mirrored to the cloud).
Cloud-native services (like AWS Lex for chatbot front-end, or Bedrock for foundation models) can accelerate development.
On the other hand, some telecoms opt for on-premises or hybrid solutions, especially for data governance reasons. Notably, ~40% of telecom firms prefer on-premises AI deployments to better control latency and data handling.
Therefore, the stack might leverage containerized AI models on-prem or use a hybrid architecture where the LLM is cloud-hosted but all customer data stays in the telco’s private environment.
Step 4: Regulatory and Ethical Considerations
Telecom operators must navigate a complex regulatory landscape when implementing AI, especially regarding data privacy, security, and transparency.
Both the United States and Canada enforce privacy laws relevant to customer communications, and telecoms are often subject to even stricter rules given the sensitive nature of phone and internet usage data.
Some of key considerations include:
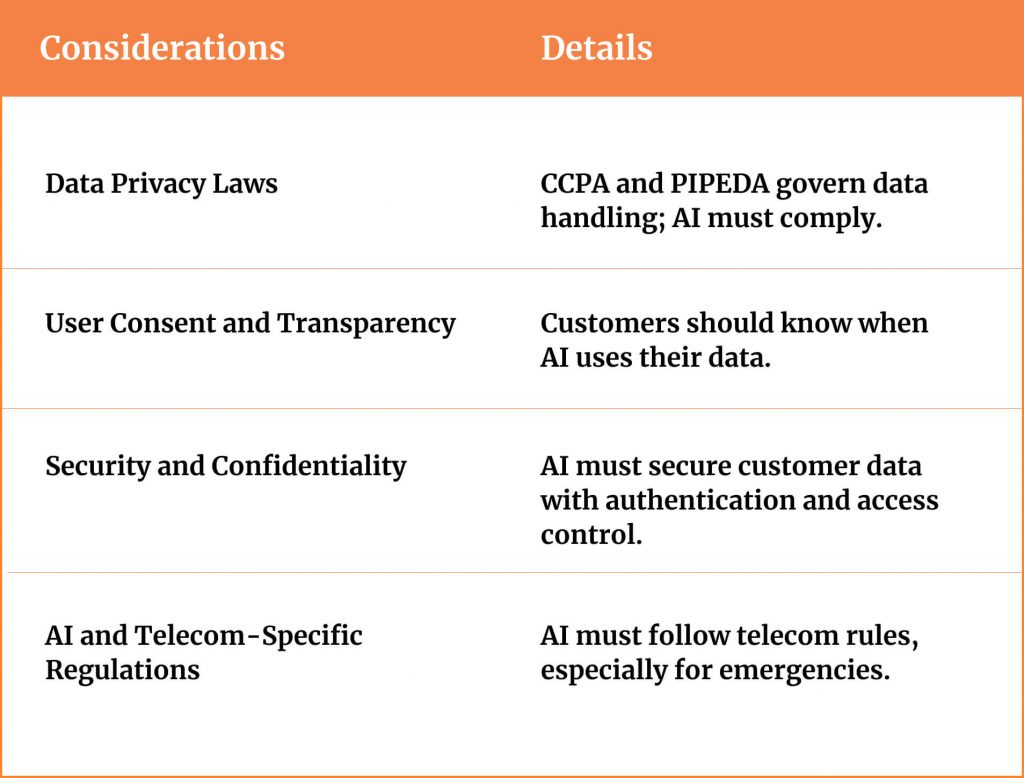
Data Privacy Laws (CCPA, PIPEDA, etc.)
In the U.S., regulations like the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) give consumers rights over their personal data usage, while in Canada the PIPEDA law governs personal data handling by companies. An AI system that accesses customer data (billing info, usage history) must comply with such laws, meaning it should only use data for the purpose the customer consented to, and it must safeguard that data.
User Consent and Transparency
Customers should be made aware when they are interacting with an AI and what data it’s using. Transparency is not just ethical but increasingly being expected by regulators. The Government of Canada’s Voluntary Code of Conduct for Generative AI specifically calls for transparency in AI interactions and decisions.
Security and Confidentiality
Telecom customer data includes call records, locations, and other highly sensitive information. Regulations often categorize some of this as CPNI (Customer Proprietary Network Information in the U.S.) which has strict rules for access and use. Any AI solution must uphold the same security standards as existing systems. This entails robust authentication and access control; the AI and its integration layer should only fetch data that the requesting user or agent is authorized to see. It also involves auditability: companies should log AI data accesses and responses in case of later disputes or regulatory audits.
AI and Telecom-Specific Regulations
Telecom is a regulated industry (FCC in the US, CRTC in Canada). While currently there may not be AI-specific telecom regulations, general principles still apply. For example, any AI-driven communication must still adhere to telecom consumer protection rules. If the AI handles emergency calls or outage info, it might step into regulated territory (e.g., 911 services have strict protocols).
Final Takeaway: Next Step in Modernizing Telecom Billing
Implementing generative AI in legacy app environments offers telecom companies a strategic path to transform customer experience in the near term.
As outlined, a thoughtfully designed AI solution can streamline customer support (e.g. explaining bills or troubleshooting devices with minimal human aid), deliver hyper-personalized interactions at scale, and continuously learn to become even more effective.
The strategic benefits are compelling:
AI augmentation leads to an improved digital experience
Customers get 24/7 instant support, clearer answers, and proactive recommendations, all of which increase satisfaction and loyalty. This kind of superior experience can set a carrier apart in a market where competitors often sell very similar products. In a saturated telecom market, customer experience is the new battleground, and companies that excel at it can gain market sharelinkedin.combain.com. By reducing pain points like billing confusion and long hold times, AI helps turn frustrated customers into promoters of the brand.
A significant competitive advantage can be gained
Early adopters of AI in telecom will develop internal expertise and data insights that laggards will struggle to catch up with. They can also market their improved service – imagine a carrier advertising “Ask our smart assistant any question about your account, anytime”.
Responsible AI implementation mitigates regulatory risk
Implementing AI with responsible principles in place can bolster trust and mitigate regulatory risks. Telecoms that take the lead in ethical AI position themselves as technology leaders and trusted service providers.
AI in legacy environments is no longer a long shot– it’s an achievable initiative with tangible benefits for telecoms.
As one industry analysis put it, AI-powered improvements in CX can lead telecom companies to grow revenues faster than the market by turning customers into enthusiastic promoters. The time to act is now: those who move into pilot gen AI solutions quick will be poised to delight customers and leapfrog competitors.
Finally, it is essential to remember that customers aren’t comparing you to other telecom companies. They’re comparing you to Apple, Amazon, and the apps they use every day. If your digital experience doesn’t meet that bar, it doesn’t matter how fast your network is.
By embracing this playbook, addressing legacy integration, focusing on valuable use cases, ensuring continuous learning, respecting regulations, and tracking success, telecom providers can unlock a new era of digital customer experience excellence.
FAQs
How can telecoms use AI to improve billing without a full system overhaul?
Generative AI can be integrated through APIs and middleware to sit on top of legacy systems, enabling natural language bill explanations and real-time support without disrupting core infrastructure.
What’s the most effective first step for AI in telecom operations?
Start with billing support. It’s a high-friction, high-volume use case that offers fast ROI, improves customer experience, and reduces support load.
How much can AI reduce billing-related call volumes?
Telecoms have reported 20–40% reductions in billing-related calls within months of deploying targeted GenAI solutions.
How secure is AI for handling sensitive telecom billing data?
When deployed responsibly, AI platforms use tokenization, encryption, and access controls while complying with laws like PIPEDA and CCPA.
What KPIs should telecoms track in an AI pilot?
Key metrics include call deflection rate, digital containment, average resolution time, CSAT, and cost-to-serve improvements.



